Test data quality in a Databricks pipeline
Use this guide as an example of how to invoke Soda data quality tests in a Databricks pipeline.
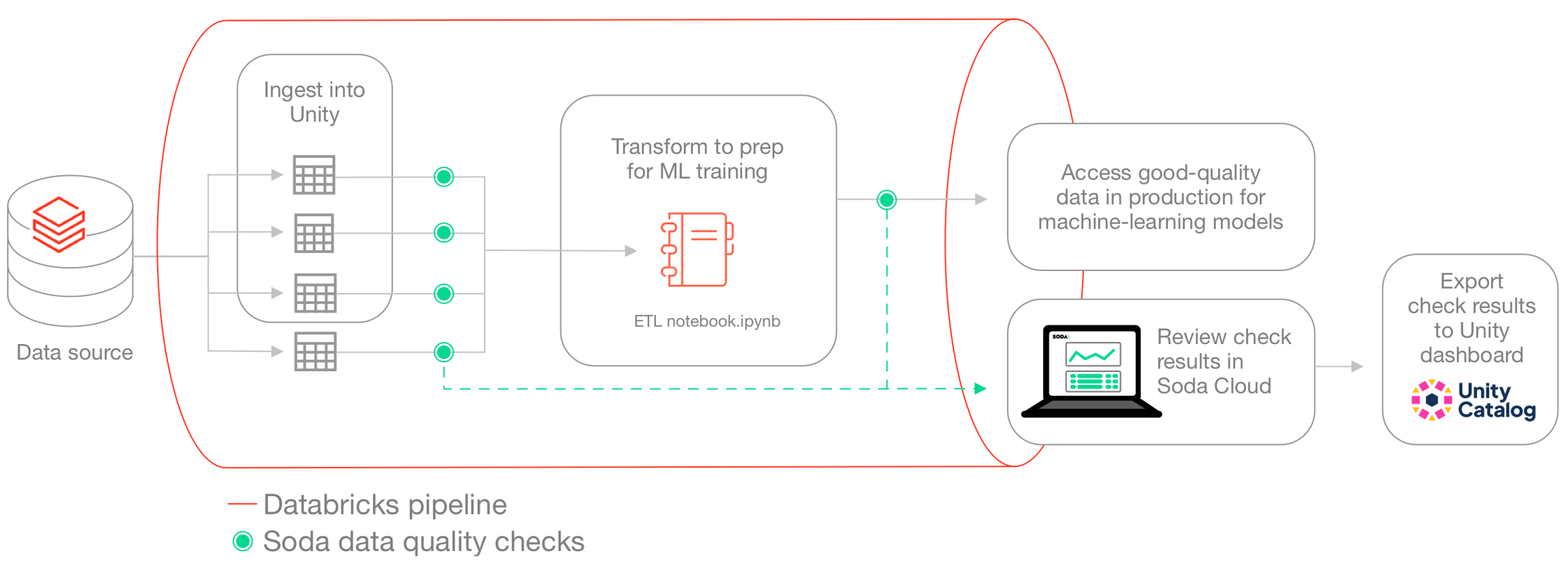
Use this guide as an example for how to set up and use Soda to test the quality of data in a Databricks pipeline. Automatically catch data quality issues after ingestion or transformation, and before using the data to train a machine learning model.
About this guide
The instructions below offers an example of how to execute Soda Checks Language (SodaCL) checks for data quality within a Databricks pipeline that handles data which trains a machine learning (ML) model.
For context, this guide demonstrates a Data Scientist and Data Engineer working with Human Resources data to build a forecast model for employee attrition. The Data Engineer, working with a Data Scientist, uses a Databricks notebook to gather data from SQL-accessible dataset, transforms the data into the correct format for their ML model, then uses the data to train the model.
Though they do not have direct access to the data to be able to resolve issues themselves, the Data Engineer can use Soda to detect data quality issues before the data model trains on poor-quality data. The pipeline the Data Engineer creates includes various SodaCL checks embedded at two stages in the pipeline: after data ingestion and after data transformation. At the end of the process, the pipeline stores the checks' metadata in a Databricks table which feeds into a data quality dashboard. The Data Engineer utilizes Databricks workflows to schedule this process on a daily basis.
Prerequisites
The Data Engineer in this example uses the following:
Python 3.8, 3.9, or 3.10
Pip 21.0 or greater
a Databricks account
access to a Unity catalog
Create a Soda Cloud account
To validate an account license or free trial, Soda Library must communicate with a Soda Cloud account via API keys. You create a set of API keys in your Soda Cloud account, then use them to configure the connection to Soda Library.
In a browser, the Data Engineer navigates to cloud.soda.io/signup to create a new Soda account, which is free for a 45-day trial.
They navigate to your avatar > Profile, access the API keys tab, then click the plus icon to generate new API keys.
They copy+paste the API key values to a temporary, secure place in their local environment.
Connect Soda Cloud to Soda Library and data source
Within Databricks, the Data Engineer creates two notebooks:
Data Ingestion Checks, which runs scans for data quality after data is ingested into a Unity catalog
Input Data Checks, which prepares data for training a machine learning model and runs data quality scans before submitting to the model for training
In the same directory as the Databricks notebooks, the Data Engineer creates a
soda_settingsdirectory to contain this configuration file, and, later, the check YAML files that Soda needs to run scans. To connect Soda to the Unity catalog, the Data Engineer prepares asoda_conf.ymlfile which stores the data source connection details.To the file, they add the data source connection configuration to the Unity catalog that contains the Human Resources data the Data Engineer uses, and the Soda Cloud API key connection configuration, then they save the file.
Read more: Use Soda Library with Spark DataFrames on Databricks
Read more: How Soda works
Write checks for data quality
A check is a test that Soda executes when it scans a dataset in your data source. The checks.yml file stores the checks you write using the Soda Checks Language. You can create multiple checks files to organize your data quality checks and run all, or some of them, at scan time.
In this example, the Data Engineer creates two checks files in the soda_settings directory in Databricks:
ingestion_checks.ymlto execute quality checks after data ingestion into the Unity catalog in the Data Ingestion Checks notebookinput_data_checks.ymlto execute quality checks after transformation, and before using it to train their ML model in the Input Data Checks notebook.output_data_checks.ymlto execute quality checks after training the model and monitor the performance of your model.
The raw data in this example is divided into two main categories.
The first category is Human Resources data, which the Unity catalog contains in three datasets: basic employee information, results of manager surveys, and results of employee surveys. The survey datasets are updated on a frequent basis.
The second category is application login data, which is a file in the Databricks file system; it is updated daily.
Download: employee_info_sample.csv
Read more: SodaCL reference
Post-ingestion checks
The Data Engineer creates a checks YAML file to write checks that apply to the datasets they use to train their ML model. The Data Ingestion Checks notebook runs these checks after the data is ingested into the Unity catalog. For any checks that fail, the Data Engineer can notify upstream Data Engineers or Data Product Owners to address issues such as missing data or invalid entries.
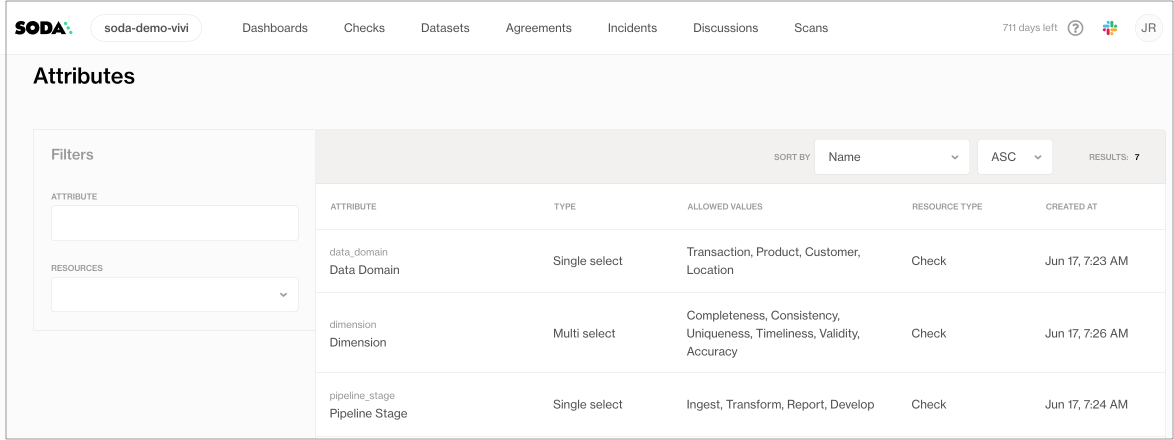
Many of the checks that the Data Engineer prepares include check attributes which they created in Soda Cloud; see image below. When added to checks, the Data Engineer can use the attributes to filter check results in Soda Cloud, build custom views (Collections), and stay organized as they monitor data quality in the Soda Cloud user interface. Skip to Review check results to see an example.
The Data Engineer also added a dataset filter to the quality checks that apply to the application login data. The filter serves to partition the data against which Soda executes the checks; instead of checking for quality on the entire dataset, the filter limits the scan to the previous day’s data.
ingestion_checks.yml
Post-transformation checks
The Data Engineer also prepared a second set of SodaCL checks in a separate file to run after transformation in the Input Data Checks notebook. Curious readers can download the ETL notebook.ipynb to review transformations and the resulting input_data_attrition_model output into a DataFrame.
Two of the checks the Data Engineer prepares involve checking groups of data. The group evolution check validates the presence or absence of a group in a dataset, or to check for changes to groups in a dataset relative to their previous state; in this case, it confirms the presence of the Married group in the data, and when any group changes. Further, the group by check collects and presents check results by category; in this case, it groups the results according to JobLevel.
input_data_checks.yml
Invoke Soda in Databricks notebooks
At the beginning of this exercise, the Data Engineer created two notebooks in their Databricks workflow:
Data Ingestion Checks to run after data is ingested into the Unity catalog
Input Data Check to run after transformation, and before using the data to train the ML model
The following outlines the contents of each notebook and the steps included to install Soda and invoke it to run scans for data quality, thereby executing the data quality checks in the checks YAMLfiles. Beyond invoking Soda to scan for data quality, the notebooks also save the checks' metadata for further analysis.
Data ingestion checks
Download: Data Ingestion Checks.ipynb
Input data checks and model output checks
Download: Input Data Checks.ipynb
Using the same structure the data scientists define some extra checks to validate and monitor the performance of their model after training. They define a ratio between the categories and apply an anomaly detection to make sure that there are no spikes or unexpected swifts in the label distribution. Furthermore, they add a check to ensure that they will notified when the model accuracy is below 60% and/or when the dataset is incomplete.
model_output_checks.yml
Review check results in Soda Cloud
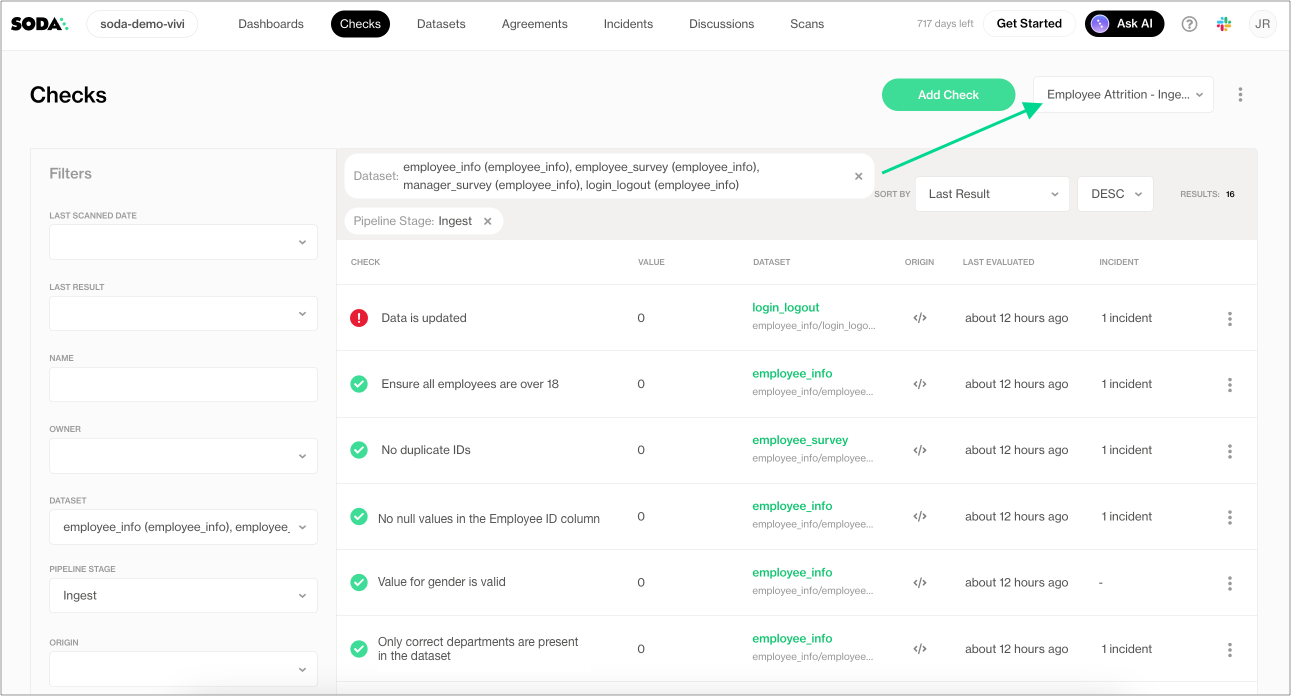
After running the notebooks, the Data Engineer accesses Soda Cloud to review the check results.
In the Checks page, they apply filters to narrow the results to the datasets involved in the Employee Attrition ML model, and distill the results even further by selecting to display only those results with the Pipeline attribute of Ingest. They save the results as a Collection labeled Employee Attrition - Ingestion to easily access the relevant quality results in the future.
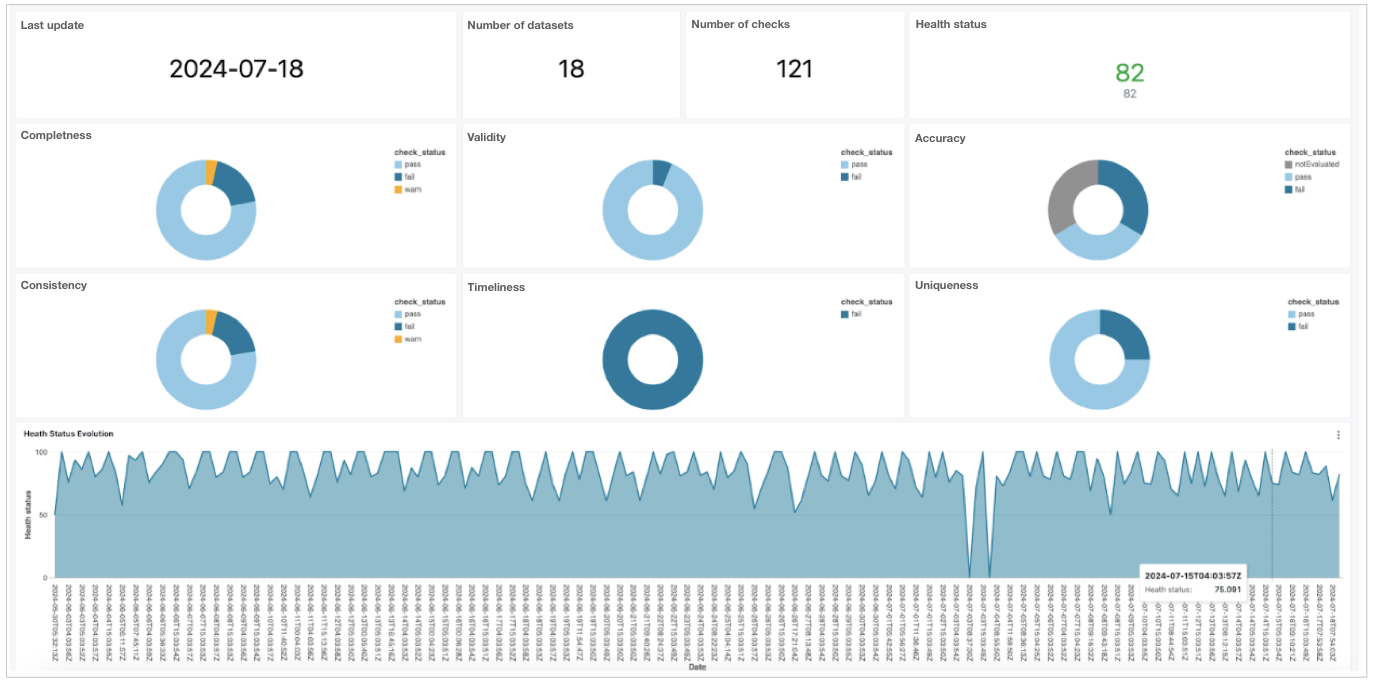
Review check results in a Unity dashboard
After the Data Engineer trains the model to forecast employee attrition, they decide to devise an extra step in the process to use the Soda Cloud API export all the Soda check results and dataset metadata back into the Unity catalog, then build a dashboard to display the results.
Coming soon: a tutorial for building a dashboard using the Soda Cloud API.
Go further
Learn more about SodaCL metrics and checks.
Learn more about getting organized in Soda Cloud.
Set notification rules to receive alerts when checks fail.
Need help? Join the Soda community on Slack.
Last updated
Was this helpful?
