Numeric metrics
Use numeric metrics in SodaCL checks for data quality.
Use a numeric metric in a check to perform basic calculations on the data in your dataset.
checks for retail_products:
- avg(size) between 100 and 300
- avg_length(manufacturer) > 10
- duplicate_count(product_id) = 0
- duplicate_percent(user_id) < 2%
- max(size) <= 500
- max_length(manufacturer) = 25
- min(size) >= 50
- min_length(manufacturer) = 5
- row_count > 0
- percentile(size, 0.95) > 50checks for retail_orders_postgres:
- stddev(order_quantity) > 0
- stddev_pop(order_quantity) between 3 and 4
- stddev_samp(order_quantity) not between 3 and 4
- sum(discount) < 120
- variance(discount) > 0
- var_pop(discount) between 0 and 5
- var_samp(discount) not between 0 and 5✖️ Requires Soda Core Scientific (included in a Soda Agent) ✔️ Supported in Soda Core ✔️ Supported in Soda Library + Soda Cloud ✔️ Supported in Soda Cloud Agreements + Soda Agent ✔️ Some available as a no-code check with a self-hosted Soda Agent connected to any Soda-supported data source, except Spark, and Dask and Pandas OR with a Soda-hosted Agent connected to a BigQuery, Databricks SQL, MS SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Redshift, or Snowflake data source
Define checks with numeric metrics
In the context of Soda check types, you use numeric metrics in Standard checks. Refer to Standard check types for exhaustive configuration details.
You can use the row_count metric in checks that apply to entire datasets.
You can use all numeric metrics in checks that apply to individual columns in a dataset. Identify the column by adding a value in the argument between brackets in the check.
You can use some numeric metrics in checks with either fixed or change-over-time thresholds. See Change-over-time thresholds for more detail.
Failed row samples
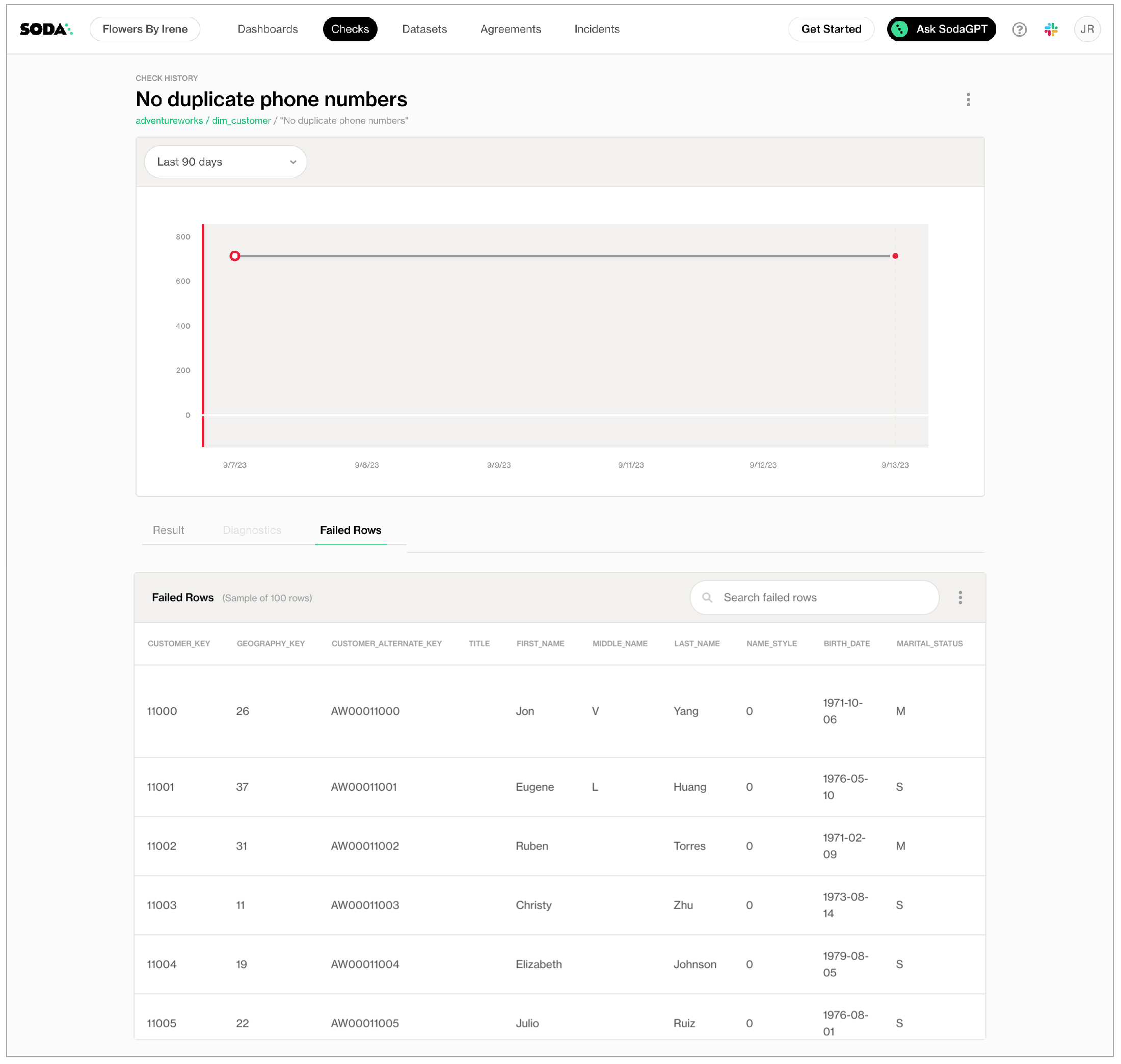
Checks that use the duplicate_count or duplicate_percent metrics automatically collect samples of any failed rows to display in Soda Cloud. The default number of failed row samples that Soda collects and displays is 100.
If you wish to limit or broaden the sample size, you can use the samples limit configuration in a check with a validity metric. You can add this configuration to your checks YAML file for Soda Library, or when writing checks as part of an agreement in Soda Cloud. See: Set a sample limit.
For security, you can add a configuration to your data source connection details to prevent Soda from collecting failed rows samples from specific columns that contain sensitive data. See: Disable failed row samples.
Alternatively, you can set the samples limit to 0 to prevent Soda from collecting and sending failed rows samples for an individual check, as in the following example.
You can also use a samples columns or a collect failed rows configuration to a check to specify the columns for which Soda must implicitly collect failed row sample values, as in the following example with the former. Soda only collects this check’s failed row samples for the columns you specify in the list. See: Customize sampling for checks.
Note that the comma-separated list of samples columns does not support wildcard characters (%).
To review the failed rows in Soda Cloud, navigate to the Checks dashboard, then click the row for a check for duplicate values. Examine failed rows in the Failed Rows Analysis tab; see Manage failed row samples for further details.
Optional check configurations
✓
Define alert configurations to specify warn and fail thresholds; see example.
✓
Apply an in-check filter to return results for a specific portion of the data in your dataset; see example.
✓
Use quotes when identifying dataset or column names; see example. Note that the type of quotes you use must match that which your data source uses. For example, BigQuery uses a backtick (`) as a quotation mark.
Use wildcard characters ( % or * ) in values in the check.
-
✓
Use for each to apply checks with numeric metrics to multiple datasets in one scan; see example.
Example with alert configuration
Example with check name
Example with in-check filter
Example with quotes
Example with dataset filter
Example with for each
List of numeric metrics
avg
The average value in a numeric column.
number
all
avg_length
The average length in a text column.
text
all
duplicate_count
The count of distinct values that have duplicates.
Multiple column names can be specified to count duplicate sets of values, as in duplicate_count(a, b)
See also: Duplicate check
number text time
all
duplicate_percent
duplicate_count (as defined above) over the total row count, expressed as a percentage.
See also: Duplicate check
number text time
all
max
The greatest value in a numeric column.
number
all
max_length
The greatest length in a text column.
text
all
min
The smallest value in a numeric column.
number
all
min_length
The smallest length in a text column.
text
all
percentile
The value below which a percentage of observations fall within a group of observations.
For example, percentile(distance, 0.7).
number
PostgreSQL Snowflake
row_count
The number of rows in a dataset or column, if specified.
number text time
all
stddev
The calculated standard deviation of values in a numeric column.
number
Athena BigQuery PostgreSQL Redshift Snowflake
stddev_pop
The calculated population standard deviation of values in a numeric column.
number
Athena BigQuery PostgreSQL Redshift Snowflake
stddev_samp
The calculated sample standard deviation of values in a numeric column.
number
Athena BigQuery PostgreSQL Redshift Snowflake
sum
The calculated sum of the values in a numeric column.
number
all
variance
The calculated variance of the values in a numeric column.
number time
Athena BigQuery PostgreSQL Redshift Snowflake
var_pop
The calculated population variance of the values in a numeric column.
number time
Athena BigQuery PostgreSQL Redshift Snowflake
var_samp
The calculated sample variance of the values in a numeric column.
number time
Athena BigQuery PostgreSQL Redshift Snowflake
List of comparison symbols and phrases
Change-over-time thresholds
This feature is not supported in Soda Core OSS. Migrate to Soda Library in minutes to start using this feature for free with a 45-day trial.
Numeric metrics can specify a fixed threshold which is not relative to any other threshold. row_count > 0 is an example of a check with a fixed threshold as the threshold value, 0, is absolute. Refer to Checks with fixed thresholds for details.
Only checks that use numeric metrics can specify a change-over-time threshold, a value that is relative to a previously-measured, or historic, value. Sometimes referred to as a dynamic threshold or historic metrics, you use these change-over-time thresholds to gauge changes to the same metric over time. Most of the examples below use the row_count metric, but you can use any numeric metric in checks that use change-over-time thresholds.
The most basic of change-over-time threshold checks has three or four mutable parts:
a metric
an argument (optional)
a comparison symbol or phrase
a threshold
The example below defines a check that applies to the entire dataset and counts the rows in the dataset, then compares that value to the preceding value contained in the Cloud Metric Store. If the row_count at present is greater than the previously-recorded historic value for row_count by more than 50 or less than -20, the check fails.
Use between for checks with change-over-time thresholds as much as possible to trigger check failures when the measurement falls outside of a range of acceptable values. This practice ensures that you get visibility into changes that either exceed or fall short of threshold expectations.
metric
row_count
threshold
between -20 and +50
You can also use use a change-over-time threshold to compare check results relative to the same day in the previous week. The example below uses change-over-time to compare today's value with the same check result from last week to confirm that the delta is greater than 10.
metric
row_count
threshold
> 10
The example below defines a check that applies to the entire dataset and counts the rows in the dataset, then compares that value to the preceding value contained in the Cloud Metric Store. If the row_count at present is greater than the previously-recorded historic value for row_count by more than 50%, the check fails.
For example, the previously-recorded historic measurement for row count is 80, and the newly-recorded value is 100, the relative change is 25%, which is less than the 50% specified in the threshold, so the check passes.
Percentage thresholds are between 0 and 100, not between 0 and 1.
If you wish, you can add a
%character to the threshold for a change-over-time threshold for improved readability.If the previous measurement value is 0 and the new value is 0, Soda calculates the relative change as 0%. However, if the previous measurement value is 0 and the new value is not 0, then Soda indicates the check as
NOT EVALUATEDbecause the calculation is a division by zero.
metric
row_count
comparison symbol
<
threshold
50 %
The example below applies to only the phone column in the dataset and counts the rows that contain duplicate values, then compares that value to the preceding value contained in the Cloud Metric Store. If the number of duplicate phone numbers at present is greater than the preceding historic values for duplicate_count by more than 20, the check fails.
metric
duplicate_count
argument
(phone)
comparison symbol
<
threshold
20
A more complex change-over-time threshold check includes two more optional mutable parts:
a calculation type (optional) avg, min, max
a historical value definition (optional) 7
percent (optional)
a metric
an argument (optional)
a comparison symbol or phrase
a threshold
The example above defines three checks, one for each type of calculation available to use, avg, min, and max, all of which apply to the entire dataset.
The first check counts the rows in the dataset, then compares that value to the calculated average of the preceding seven measurement values for that metric contained in the Cloud Metric Store. If the row_count at present is greater than the average of the seven preceding historic values by more than 50, the check fails. The only valid historical value definition you can use is seven.
calculation type (optional)
avg
a historical value definition (optional)
last 7
percent (optional)
-
metric
row_count
argument (optional)
-
comparison symbol or phrase
<
a threshold
50
The second check in the example determines the minimum value of the preceding seven historic values, then uses that value to compare to the present measurement value.
calculation type (optional)
min
historical value definition (optional)
last 7
percent (optional)
-
metric
row_count
argument (optional)
-
comparison symbol or phrase
<
a threshold
50
The third check in the example determines the maximum value of the preceding seven historic values, then uses that value and the present measurement value to calculate the percentage of change.
calculation type (optional)
max
historical value definition (optional)
last 7
percent (optional)
percent
metric
row_count
argument (optional)
-
comparison symbol or phrase
<
a threshold
50
Go further
Use numeric metrics in checks with alert configurations to establish warn and fail zones
Use numeric metrics in checks to define ranges of acceptable thresholds using boundary thresholds.
Reference tips and best practices for SodaCL.
Need help? Join the Soda community on Slack.
Last updated
Was this helpful?
